There’s something magical that happens when you pause—just for a moment—and breathe in gratitude. The world doesn’t change instantly… but you do. The edges soften. The noise quiets. Your heart opens just a little wider. And suddenly, the ordinary becomes extraordinary.
When you pair this daily practice with the gentle support of doTERRA’s pure tested-grade essential oils, that magic becomes even more tangible. Aromatic molecules meet mindful intention, and together they create openings for joy, peace, clarity, and presence.
This month, I’ve been leaning deeply into this pairing—gratitude + aroma—and I’m excited to share these simple, soul-nourishing practices with you.
Why Gratitude + Aroma Work So Beautifully Together
Gratitude anchors you. Essential oils activate your senses. Together, they shift your emotional state in seconds. While journaling or speaking gratitude aloud engages the mind, aromatic blending communicates directly with the limbic system—your emotional command center—helping the heart and body catch up with what your mind already knows:
There is beauty here.
There is blessing here.
There is enough.
You are enough.
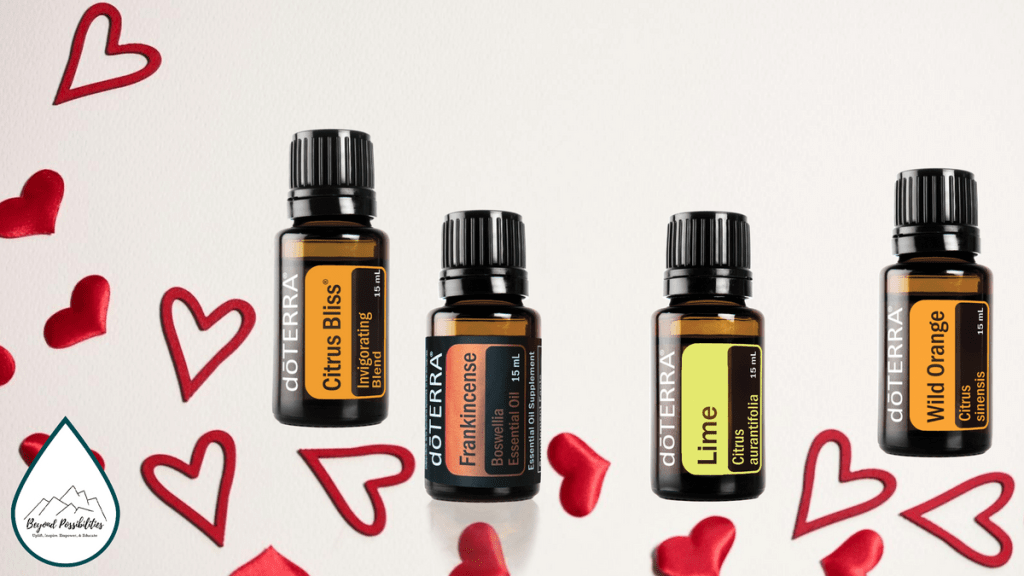

Aromatic Companions for a Grateful Heart
Below are some of my favorite doTERRA blends and single oils for building or deepening your gratitude practice—each one supporting the heart, mind, and breath in a different, beautiful way.
✨ Citrus Bliss® — The Joy Igniter
There’s a reason we instinctively smile when we smell citrus. Citrus Bliss blends wild orange, lemon, grapefruit, mandarin, bergamot, tangerine, and vanilla—inviting a burst of sunshine into your day.
Use it when:
You want to feel brighter, lighter, or inspired. Add a drop to your palms, inhale deeply, and speak three things you’re grateful for aloud.
Why:
Citrus oils have uplifting and energizing aromatic properties that support emotional rejuvenation and promote positive feelings (doTERRA, 2023a).
✨ Balance® — The Grounding Blend
Balance feels like stepping onto soft earth after a long day. Spruce, frankincense, blue tansy, ho wood, and osmanthus work together to create a calming, steadying aroma.
Use it when:
Your mind is racing, your emotions feel scattered, or you want to reconnect with the present moment.
Why:
Tree oils contain grounding aromatic constituents that can help the mind and body experience greater calm and stability (doTERRA, 2023b).
✨ Frankincense — The Heart Opener
Frankincense has long been known as the “oil of truth,” and for good reason. Its rich, resinous aroma encourages deeper breathing and a fuller sense of connection—both inward and upward.
Use it when:
You’re journaling, reflecting, praying, or giving thanks for something tender or powerful.
Why:
Frankincense’s centering and focusing aromatic compounds support emotional balance and deeper reflection (Buckle, 2015).

✨ Spikenard — The Deep-Rooted Stillness Oil
Spikenard carries an ancient, grounding aroma—earthy, warm, and quietly powerful. It invites you to slow everything down and listen beneath the noise.
Use it when:
You crave deeper stillness, spiritual grounding, or a moment to reconnect with your inner wisdom.
Why:
Spikenard’s soothing aromatic profile is traditionally used to promote relaxation, calm, and emotional centering (doTERRA, 2023c).
✨ Helichrysum — The Emotional Renewal Oil
Known as the “Everlasting” or “Immortelle” flower, Helichrysum encourages emotional resilience. It’s gentle, comforting, and incredibly supportive when gratitude feels just out of reach.
Use it when:
You’re healing, releasing emotional patterns, or wanting a fresh, hopeful mindset.
Why:
Helichrysum’s aromatic compounds have long been associated with renewal, comfort, and emotional support (doTERRA, 2023d).
✨ Lime — The Bright-Hearted Encourager
Lime’s vibrant, lively aroma brings clarity and forward motion. It’s perfect for mornings or moments when you want to cultivate optimism.
Use it when:
You’re setting intentions, starting your day, or need a little spark of energy.
Why:
Citrus oils like lime offer uplifting and energizing aromatic benefits that help cultivate positive emotional states (doTERRA, 2023e).
✨ Beautiful® Body Mist — The Worthiness Whisper
With Bergamot, Lime, Frankincense, and Osmanthus, Beautiful® is the blend that reminds you of your own inner light. The body mist turns gratitude into a whole-body, sensory experience.
Use it when:
You want to feel grounded in your body, uplifted in your mindset, or wrapped in a moment of self-worth.
Why:
Beautiful® was crafted to evoke feelings of radiance, courage, and self-compassion, promoting emotional wellbeing through its bright yet grounding aromatic blend (doTERRA, 2023f).
✨ Harvest Spice® — The Cozy Gratitude Blend
Warm, nostalgic, and deeply comforting, Harvest Spice® brings feelings of connection and belonging. It’s gratitude in aromatic form.
Use it when:
You’re cultivating family connection, celebrating blessings, or creating a cozy environment for reflection.
Why:
Spice oils have warming and uplifting qualities that promote comfort, joy, and togetherness (doTERRA, 2023g).
✨ Wild Orange — The Spark of Joy
Wild Orange is the essence of optimism. Its sweet, bright aroma makes gratitude feel effortless.
Use it when:
You want to amplify joy, reset your mood, or add brightness to your gratitude journal or diffuser practice.
Why:
Wild Orange’s energizing and mood-enhancing aromatic compounds inspire feelings of joy, creativity, and positivity (doTERRA, 2023h).
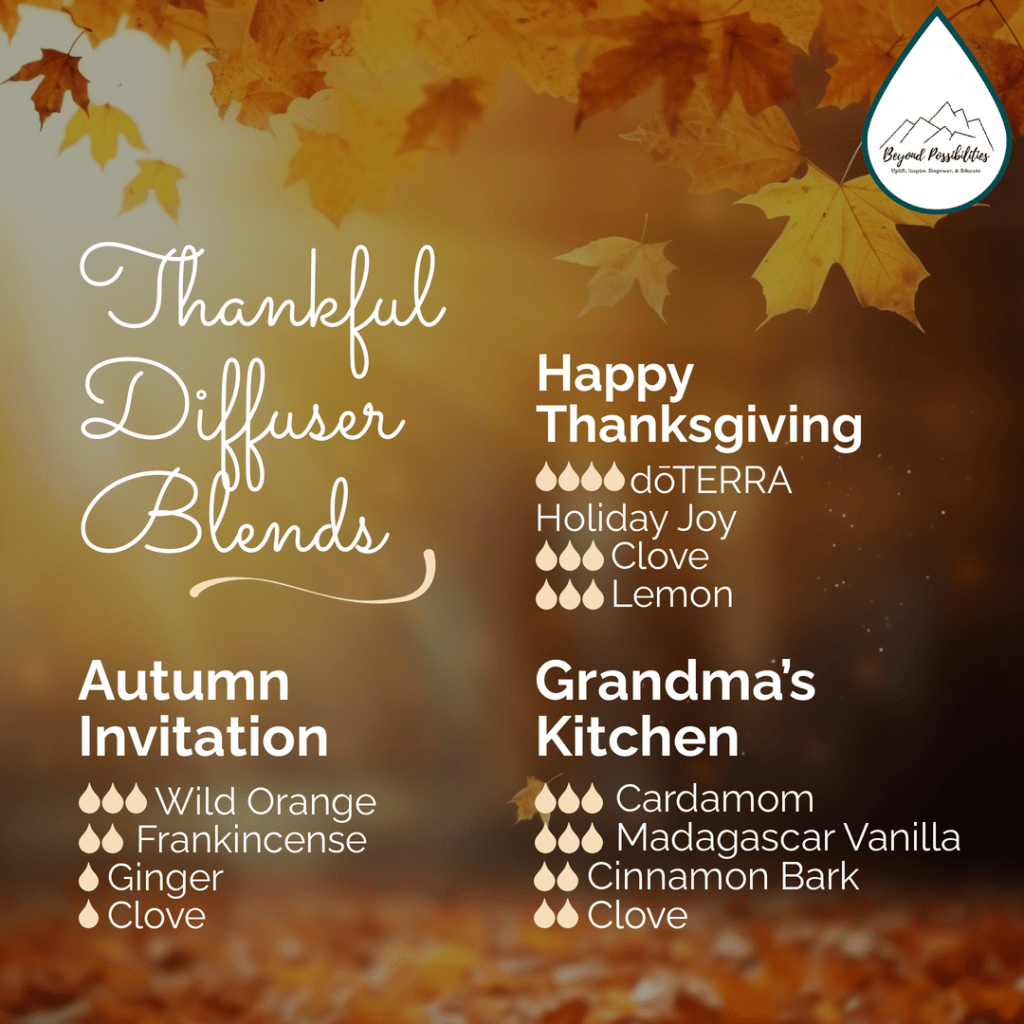
Gratitude Diffuser Blends
If you want to elevate your gratitude practice even more, consider creating a gratitude “atmosphere” in your home or workspace. Diffusing blends with citrus, woods, spices, and resins can shift your emotional state before you ever pick up a pen or whisper a thank-you. These aromas bring warmth, expansion, and presence into the air around you—making gratitude feel more natural, accessible, and embodied.



A Simple Daily Gratitude Ritual
Try this practice for a week and notice the shift:
- Choose your oil. Pick the one your heart needs today: Joy, grounding, stillness, renewal, or brightness.
- Breathe it in. One deep inhale with your hand over your heart.
- Speak or write one thing you’re grateful for today.
- Close with a grounding exhale.
- Carry the aroma—and the gratitude—with you.
Five steps. One minute. A completely different day.

When Ordinary Becomes Extraordinary
Here’s what I’ve learned after years of helping others reconnect with themselves:
Gratitude doesn’t ignore the hard things.
It simply helps you remember the good things, too.
And essential oils don’t fix your life.
But they can shift your energy, soften your breath, and help your heart receive what your mind already knows:
There is still wonder.
There is still goodness.
There is still so much to be grateful for.
Whether you’re, starting a journal practice, a pro at gratitude, or simply pausing to appreciate what’s right in front of you, know this:
Every single breath of gratitude opens the door to an extraordinary life.
One moment… one aroma… one blessing at a time.
References (APA 7)
Buckle, J. (2015). Clinical aromatherapy: Essential oils in healthcare (3rd ed.). Elsevier.
doTERRA. (2023a). Citrus Bliss® essential oil blend. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023b). Balance® grounding blend. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023c). Spikenard essential oil. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023d). Helichrysum essential oil. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023e). Lime essential oil. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023f). Beautiful® body mist. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023g). Harvest Spice® essential oil blend. https://www.doterra.com
doTERRA. (2023h). Wild Orange essential oil. https://www.doterra.com